Dopamine Design
In the digital world, dopamine - our "happiness hormone" - has a significant influence on how users react to online experiences. Platforms, apps and brands deliberately use mechanisms such as dark patterns, gamification and reward loops to attract attention and retain users. But where is the line between clever design and manipulative practice? More and more companies are recognising that responsible dopamine design is not only ethical, but also promising in the long term.
Responsible design
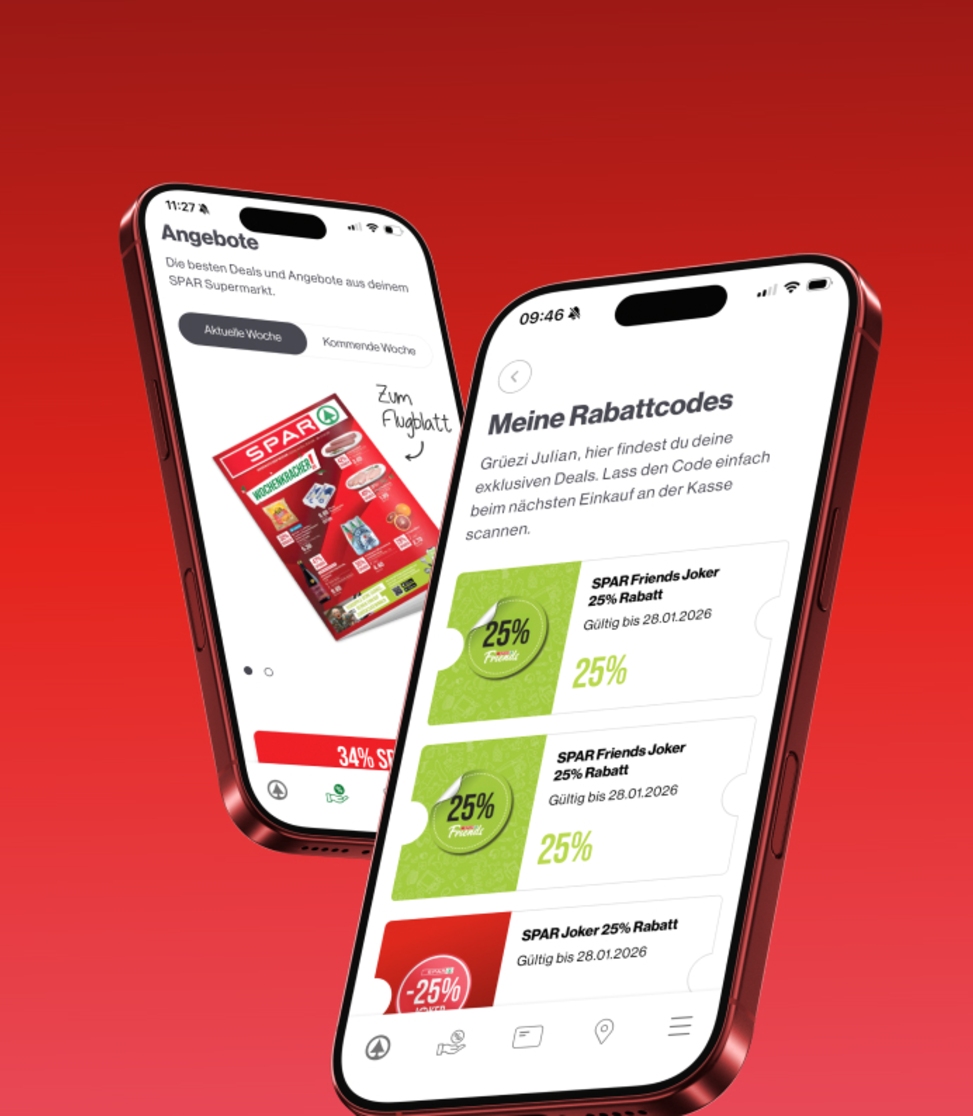
Dark patterns are manipulative design tricks that unconsciously tempt users to make decisions that they don't actually want to make - for example through hidden costs, complicated cancellations or automatically activated subscriptions. Such methods damage trust in the long term and should have no place in responsible dopamine design.
Instead, brands should focus on transparency, freedom of choice and fair incentives. Gamification motivates in a playful way without overtaxing, and reward loops provide meaningful rewards without being addictive. This creates a win-win situation: users feel valued and brands benefit from loyal customers.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
Dopamine design describes digital design that specifically appeals to the brain's reward system - for example through playful elements, rewards or personalised content - in order to activate and retain users.
No. Dopamine design can be used responsibly to promote positive user experiences. It only becomes manipulative when users are deliberately pressurised into making decisions or addictive mechanisms are used - such as dark patterns.
Dark patterns are manipulative design tricks that trick users into taking actions that they would not consciously take - e.g. hidden costs, hard-to-find cancellations or automatically activated subscriptions.
When used correctly, dopamine design creates motivation, orientation and enjoyment: gamification can lead to more interaction, reward loops retain users in the long term, and microinteractions ensure intuitive operation and feedback.
By ensuring transparency, freedom of choice and fair incentives. Users should understand how mechanisms work and be able to make their own decisions at any time - this creates trust and long-term customer loyalty.